Acer saccharum
Leaves are opposite simple.
 The
sugar maple (hard maple, rock maple) is one of our largest and finest forest trees, growing to a
feet with a diameter of 2 or more feet. The tree produces a dense, round, compact crown when grown
in the open and is used quite extensively as a shade or ornamental tree. In the fall the yellow,
red and crimson colors of the leaves form a very showy and beautiful part of the landscape. It is
the best of the maples for production of maple syrup and sugar.
The
sugar maple (hard maple, rock maple) is one of our largest and finest forest trees, growing to a
feet with a diameter of 2 or more feet. The tree produces a dense, round, compact crown when grown
in the open and is used quite extensively as a shade or ornamental tree. In the fall the yellow,
red and crimson colors of the leaves form a very showy and beautiful part of the landscape. It is
the best of the maples for production of maple syrup and sugar.
It is found throughout southeastern Canada, the eastern United States and as far west as central Iowa.
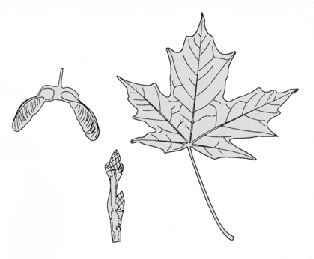
The leaves are three to five lobed, but usually five lobed. The lobes are deeply cut with rounded divisions between the lobes, dark green above and pale green with a silvery cast below.
The twigs are opposite on the stem, smooth and gray to brown in color.
Similar to other maples, the fruit is a pair of winged seeds about 1 inch long. The seeds ripen in the autumn.
On large branches and trunk the bark is light to dark gray, narrowly ridged with long, deep furrows, sometimes becoming scaly.
 Leaves:
Leaves:
- Five main lobes.
- Margin (edge) of leaf is entire (not serrated).
- The margins of the central lobe are parallel.
- Notches between the lobes are moderately deep.
- Palmately veined.
- Base of lobes are rounded.
- Turn yellow, orange, and scarlet in the fall.
Bark: dark gray. As the tree matures, the bark becomes deeply fissured (looks shaggy).
Height: 60 to 80 ft.
Trunk Diameter: 1 to 3 ft.
Longevity: 200 to 300 yrs.
Tolerance: extremely tolerant
Range: eastern U.S. as far south as Tennessee
Fun Facts:
- Maple syrup is made from the sap.
- Lumber used for furniture and bowling alleys.
- It takes about 40 gallons of sap to make one gallon of maple syrup.
![]()